Adjuvant radiotherapy for synovial sarcoma of the hand: a case report and literature review
Introduction
Malignant fibrous histiocytoma, liposarcoma, and rhabdomyosarcoma are the three most common types of sarcoma, and synovial sarcoma—a rare and aggressive soft tissue sarcoma—is the fourth most common, accounting for 5–8% of soft tissue sarcomas. It typically develops in young adults as well as adolescents. Despite its nomenclature, synovial sarcoma lesions are not usually intra-articular but instead develop near tendon sheaths, bursae, and joint capsules (1). Signs or symptoms may not be noticeable in the early stages; however, with an increase in tumor size over time, individuals with synovial sarcoma may discover that they have a lump or swelling. For some individuals, range of motion may be limited by the mass and numbness and/or pain may be caused due to the compression of nerves in the locality. The exact cause of synovial sarcoma has not yet been identified, but the disease’s development is believed to be affected by genetic factors. Translocation t(X;18) characterizes synovial sarcoma cytogenetically; it is specific to this cancer type and frequently employed for diagnostic purposes. Although surgery and radiation therapy can result in comprehensive local control, survival is still limited by the prevalence of distant metastasis. Among those who have ≥5 cm synovial sarcoma in a primary extremity, distant metastasis is discovered in more than half of patients, and mortality occurs within 5 years in nearly two-fifths of such patients (2,3). A combination treatment is generally employed that comprises surgery, radiation therapy, and/or chemotherapy (4). Even if initial treatment is aggressive, with a wide surgical resection and multiple adjuvant treatments, local recurrence and metastasis often occur and oncologists are cautious in their prognoses.
Case presentation
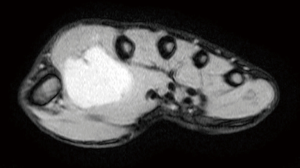
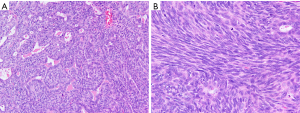
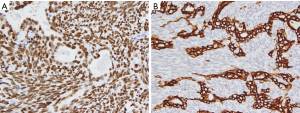
This case report relates to a 22-year-old male patient with synovial sarcoma, who had a painful mass in right thenar region that he had been aware of for approximately 3 years before he sought medical treatment. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed a nodular mass localized at the volar aspect of the palm between the first and second finger, with the mass measuring 5×3×3 cm3 (Figure 1). At that time, chest computed tomography (CT)-scan was negative. He was treated with en bloc resection on September 21, 2017. Histologically, epithelial and spindle-cell components were present in varying proportions. The epithelial cells were arranged in solid nests, cords, or glands with a tubular, alveolar, or papillary architecture. The spindle cells were fairly uniform, in dense cellular sheets or vague fascicles. Focal fibrosis and myxoid change were also noted. In glandular areas, the epithelial cells were cuboidal and had ovoid vesicular nuclei and abundant, palely eosinophilic cytoplasm. The spindle cells had sparse cytoplasm, ovoid and bland but also hyperchromatic nuclei, and inconspicuous nucleoli (Figure 2). FNCLCC (Federation Nationale des Centres de Lutte Contre le Cancer) Grade 2 with a total score of 5 was obtained. The surgical margin was considered to be positive due to fragmented tissue. Immunohistochemical stains revealed strong positivity for transducer-like enhancer of split 1 (TLE1) and focal positivity for cytokeratin (AE1 + AE3) (Figure 3). Other stains revealed that the patient was negative for CD34, S-100 protein, myeloperoxidase (MPO), and desmin. Afterwards, in an attempt to gain local control, the patient was referred to the radiation oncology department for radiotherapy.
Thermoplastic cast was used for immobilization of the patient during radiotherapy. We outlined the index finger and the thumb of the patient for each CT slice scan; therefore, the compartment was assumed to be the clinical target volume (CTV). The CTV was isotropically extended by 1 cm to define the planning target volume (PTV) (Figure 4). Synovial sarcoma is known to sometimes invade skin tissues. For routine skin dose assessment, Gafchromic EBT3 film measuring 3×3 cm2 was used for in vivo dosimetry to verify the dose to skin. In this case, the patient’s right hand was immersed in a water tank and subjected to irradiation using a bilateral photon beam of energy 6 MV (Figure 5). Thirty fractions of 2 Gy were administered, resulting in a total dose of 60 Gy. The Philips pinnacle version 9.8 was the treatment planning system employed. We selected the palm (point A) and back of the hand (point B) as the two points for assessment and repeated the measurement once daily for 3 days. The average skin dose at points A and B was 220.9±2.2 and 219.6±1.2 cGy, respectively. The planned doses at points A and B were 216.2 and 217.0 cGy, respectively; thus, the actual delivered treatment dose were 1.9% and 2.2% higher than the planned amounts. This study demonstrated that employing a water tank to act as a tissue compensator results in skin tissues receiving sufficient doses. The patient tolerated the treatment very well, and grade I dermatitis was the only observed side effect. MRI performed 4 months after completion of radiotherapy indicated a 0.6 cm nodule at the volar aspect of the palm, which was not the original site of the disease. Consequently, further MRI study is indicated for confirmation of recurrence.


Discussion
The optimal treatment of synovial sarcoma is undefined at the present time, but en bloc tumor resection is the current first-choice treatment. A minimum requirement of surgical treatment is that the pathologic specimen must be tumor-free at the margin. The difference between complete local resection and wide tumor resection appears to significantly influence outcome (5). Noncurative surgery—for example, intralesional excisions or an incomplete gross resection—should have no part in treatment (6,7). Surgery is nonetheless the most commonly employed modality for treatment of locally recurrent disease, as it is for treatment of primary disease (8,9). Adjuvant radiation therapy is employed in synovial sarcoma under the same rationale as it is employed in soft tissue sarcomas (6,7). Adjuvant radiation therapy modalities include brachytherapy, conventional two-dimensional radiotherapy, and intensity-modulated radiation therapy. The local control rate in patients with high-grade sarcomas such as synovial sarcoma has been demonstrated to be higher when radiation therapy is employed, irrespective of the radiation therapy type (10,11). The various international guidelines have inconsistent recommendations regarding radiotherapy dose. In one study, 61.2 Gy (range, 45–66.6 Gy) was discovered to be a sufficient dose in adjuvant radiotherapy, with 5-year overall survival being 77% and 10-year overall survival being 65% (12). However, that local irradiation is associated with superior local control of the disease in patients with localized, completely resected tumor and negative surgical margin is yet to be adequately demonstrated. By contrast, radiotherapy appears to significantly reduce local recurrence rates in patients with gross residual tumor after surgery. Regarding treatment order, preoperative radiotherapy appears to result in similar local control and long-term physical function as does postoperative radiotherapy. A crucial effect of timing does exist, however: postoperative wound complications are more likely to occur if radiotherapy is performed preoperatively. A more palliative approach when treating a patient with a nonresectable, localized tumor is hypofractionation—for example, 13 to 15 fractions of 3 Gy—although the suitability of this approach is dependent on factors such as patient age and comorbidities (13). The role of adjuvant chemotherapy in synovial sarcoma—a particularly chemoreactive soft tissue sarcoma—remains controversial (14,15).
Acknowledgments
Funding: None.
Footnote
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical Statement: The authors are accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee(s) and with the Helsinki Declaration (as revised in 2013). Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this manuscript and any accompanying images.
Open Access Statement: This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), which permits the non-commercial replication and distribution of the article with the strict proviso that no changes or edits are made and the original work is properly cited (including links to both the formal publication through the relevant DOI and the license). See: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
References
- Sessions WM, Siegel HJ, Casillas MA. Pitfalls in the diagnosis and management of synovial sarcoma. In: The Mid-America Orthopaedic Association Proceedings, 2004: 16-20.
- Hong L, Alektiar KM, Hunt M, et al. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy for soft tissue sarcoma of the thigh. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2004;59:752-9. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Lewis JJ, Antonescu CR, Leung DH, et al. Synovial sarcoma: a multivariate analysis of prognostic factors in 112 patients with primary localized tumors of the extremity. J Clin Oncol 2000;18:2087-94. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Ryan CW, Meyer J. Clinical presentation, histopathology, diagnostic evaluation, and staging of soft tissue sarcoma. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-presentation-histopathology-diagnostic-evaluation-and-staging-of-soft-tissue-sarcoma#H12227247
- Lewis JJ, Antonescu CR, Leung DH, et al. Synovial sarcoma: a multivariate analysis of prognostic factors in 112 patients with primary localized tumors of the extremity. J Clin Oncol 2000;18:2087-94. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Brennan MF, Lewis JJ, editors. Diagnosis and management of soft tissue sarcoma. London, United Kingdom: Martin Dunitz Ltd, 2002:123-8.
- Okcu MF, Munsell M, Treuner J, et al. Synovial sarcoma of childhood and adolescence: a multicenter, multivariate analysis of outcome. J Clin Oncol 2003;21:1602-11. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Eilber FC, Brennan MF, Riedel E, et al. Prognostic factors for survival in patients with locally recurrent extremity soft tissue sarcomas. Ann Surg Oncol 2005;12:228-36. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Eilber FC, Rosen G, Nelson SD, et al. High grade extremity soft tissue sarcomas: Factors predictive of local recurrence and its effect on morbidity and mortality. Ann Surg 2003;237:218-26. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan B, Davis AM, Turcotte R, et al. Preoperative versus postoperative radiotherapy in soft-tissue sarcoma of the limbs: a randomised trial. Lancet 2002;359:2235-41. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Pisters PW, Harrison LB, Leung DH, et al. Long-term results of a prospective randomized trial of adjuvant brachytherapy in soft tissue sarcoma. J Clin Oncol 1996;14:859-68. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Song S, Park J, Kim HJ, et al. Effects of adjuvant radiotherapy in patients with synovial sarcoma. Am J Clin Oncol 2017;40:306-11. [Crossref] [PubMed]
-
Scandinavian Sarcoma Group SSG XXIV Recommendations for Radiotherapy in Bone- and Soft Tissue Sarcoma 2015 . Available online: http://www.ssg-org.net/wp-content/uploads/2011/05/SSG-RT-Guidelines-December-2015.pdf - Kampe CE, Rosen G, Eilber F, et al. Synovial sarcoma: A study of intensive chemotherapy in 14 patients with localized disease. Cancer 1993;72:2161-9. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Rosen G, Forscher C, Lowenbraun S, et al. Synovial sarcoma: Uniform response of metastases to high dose ifosfamide. Cancer 1994;73:2506-11. [Crossref] [PubMed]
Cite this article as: Wang NT, Lui LT, Shaw S, Lin YC, Lee HY, Wu CJ. Adjuvant radiotherapy for synovial sarcoma of the hand: a case report and literature review. Ther Radiol Oncol 2018;2:34.